Summary
Organizations expect to see consistency in their decisions of their employees, but humans are unreliable. Algorithm can reduce noise. Although algorithms may seem daunting to construct, build them with input data on a small number of cases and a little common sense rules, can help to set up procedures and practices that will guide employees to make more-consistent decisions.
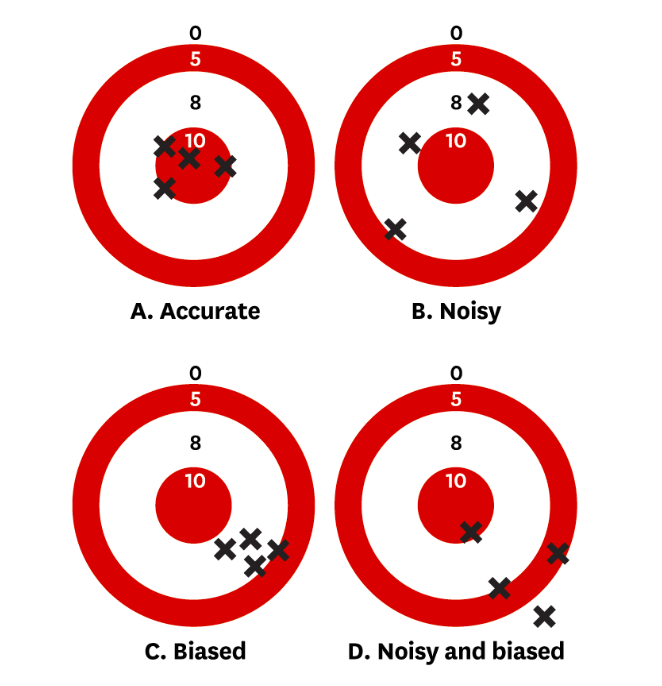
Noise in data and human judgment presents significant challenges in the realm of data analysis, as it can distort insights and lead to inaccurate conclusions. Noise refers to random variations or irrelevant information that obscures meaningful patterns within the data. In human judgment, cognitive biases and emotional factors can introduce additional noise, complicating decision-making processes. Addressing these challenges requires both technical and behavioral strategies to reduce bias during data analysis.
One approach to reducing bias during data analysis is through rigorous data preprocessing techniques. This involves cleaning the data to remove errors, outliers, and irrelevant information that may introduce noise. Additionally, data normalization methods can help standardize variables, reducing the impact of scale differences and making comparisons more meaningful.
Furthermore, employing robust statistical methods can mitigate the effects of noise in the data. Techniques such as bootstrapping, which involves repeatedly resampling the data with replacement, can provide more reliable estimates of parameters and reduce the influence of outliers. Similarly, using ensemble methods in machine learning, which combine multiple models to improve accuracy and robustness, can help mitigate the impact of noise in predictive modeling tasks.
In addition to technical approaches, fostering a culture of skepticism and critical thinking within the data analysis team is crucial for reducing bias. Encouraging analysts to question assumptions, challenge their own interpretations, and consider alternative explanations can help mitigate the effects of cognitive biases such as confirmation bias or anchoring.
Moreover, promoting diversity and inclusivity within the data analysis team can help mitigate bias by bringing different perspectives to the table. By incorporating input from individuals with diverse backgrounds and experiences, organizations can reduce the risk of groupthink and ensure that a wide range of viewpoints are considered during the analysis process.
Overall, reducing bias during data analysis requires a combination of technical expertise, critical thinking skills, and a commitment to diversity and inclusion. By implementing these strategies, organizations can improve the reliability and accuracy of their data-driven decision-making processes.
Source Daniel Kahneman, Andrew M. Rosenfield, Linnea Gandhi, and Tom Blaser From: “Noise” Oct. 2016
Contact.
Have a question? Feel free to send an email or if you prefer a virtual meeting